Overview
The Data Integration Process defines the standardized approach for collecting, enriching, curating, and delivering data into the Enterprise Data Lakehouse. It ensures data accuracy, reliability, governance, and suitability for analytics, reporting, applications, and advanced analytical use cases.
This framework supports scalable data ingestion, transformation, and consumption while aligning with cloud-native ELT principles and organizational data governance standards.
Data Integration Lifecycle
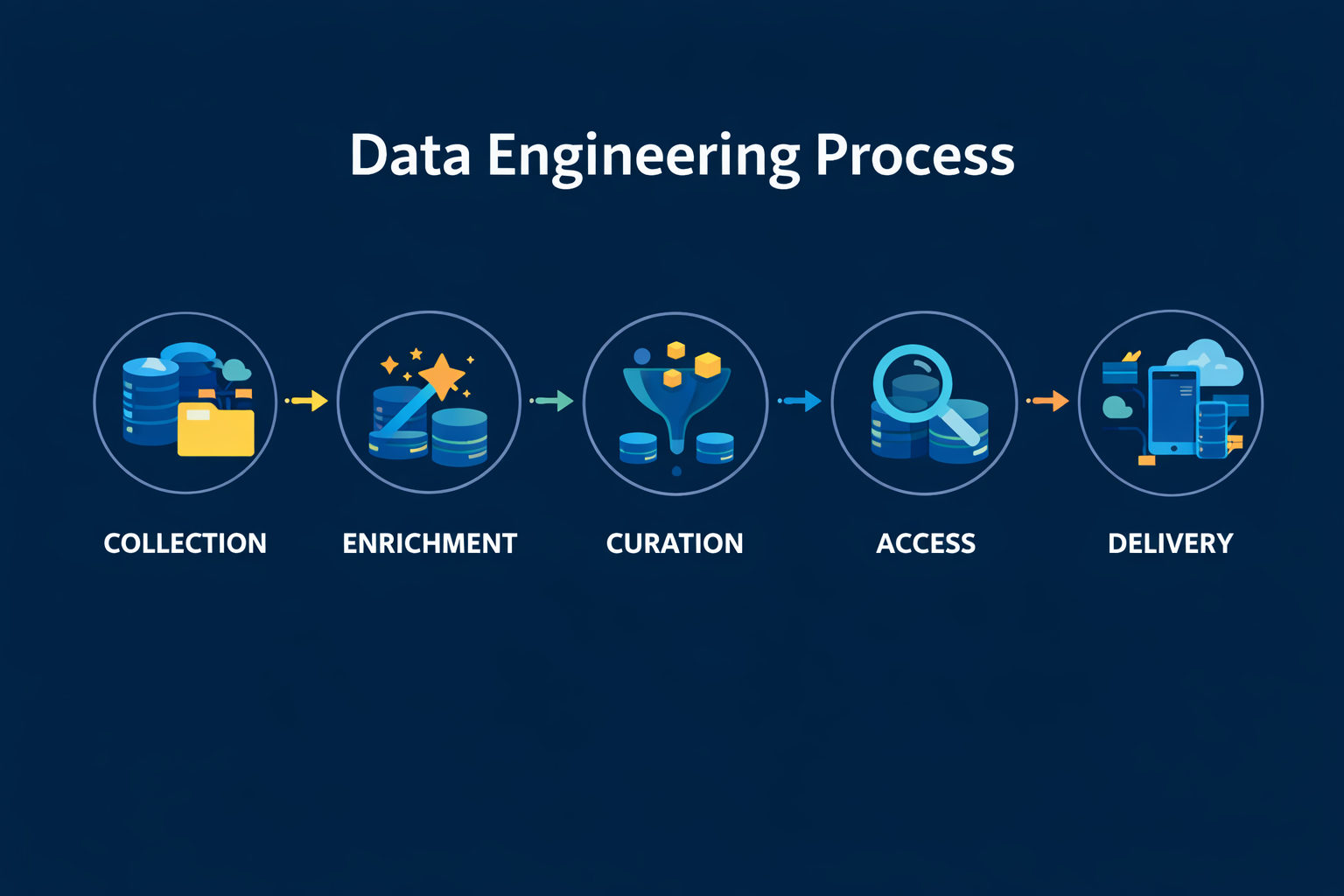
The Data Integration Process is organized into five key phases:
- Data Collection
- Data Enrichment
- Data Curation
- Data Access
- Data Delivery
Each phase is governed by defined controls, standards, and automation mechanisms to ensure operational consistency and auditability.
Phase 1: Data Collection
Data Collection is the foundational phase of the process and involves extracting data from internal and external sources and loading it into the Data Lakehouse in its raw form.
Data sources include, but are not limited to:
- On-premises relational databases (e.g., SQL Server, DB2)
- SaaS platform APIs
- Application, server, and event logs
- File-based data (CSV, JSON, Parquet, XML)
- External data providers and partners
Data is collected with minimal transformation and stored in the Landing Zone, preserving source fidelity and enabling downstream processing.
Phase 2: Data Enrichment
The Data Enrichment phase enhances raw data with technical and operational metadata to improve usability, traceability, and quality.
Key enrichment activities include:
- Metadata augmentation (source identification, ingestion timestamps, batch identifiers)
- Minimal data standardization and normalization
- Uniqueness enforcement
- Enforce data consistency from source to target
- Ability to retain historical snapshots
Enriched data is stored in the Enriched Zone and is suitable for exploratory analysis and internal analytical use cases.
Phase 3: Data Curation
Data Curation applies business logic, transformations, and validation rules to enriched datasets to produce trusted, consumption-ready data assets.
This phase ensures:
- Consistent application of business rules
- Standardized metrics and dimensions
- Compliance with data quality and governance standards
Curated datasets are stored in the Curated Zone and serve as the authoritative source for enterprise reporting and downstream consumption.
Phase 4: Data Access
The Data Access phase defines how enriched and curated datasets are securely exposed to users and systems through standardized access patterns.
Data access mechanisms include:
- Secure data sharing
- Application and API-based access
- Reporting and Analytical tools
- Data science and advanced analytics platforms
Access is governed through the Data Access Layer to ensure security, performance, and consistency.
Phase 5: Data Delivery
The final phase focuses on delivering data to authorized consumers for operational and analytical use.
Primary data consumers include:
- Enterprise applications and external vendors
- Deliver data to API end points (like Everbridge)
Data delivery mechanisms are aligned with enterprise security, compliance, and performance requirements.
Data Orchestration & Governance
All data pipelines are orchestrated through automated, schedule-driven workflows based on source system availability. Monitoring, error handling, and recovery mechanisms are implemented to ensure operational reliability.
The Data Integration Process adheres to established governance principles, including:
- ELT-first design for scalability
- Preservation of raw data
- Separation of technical enrichment and business logic
- Controlled access to curated datasets

